PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
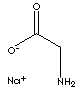
227-842-3
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
Oral rat LD50 7930 mg/kg
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
pH
REFRACTIVE INDEX
APPLICATIONS
Flavor enhancers and maskers, pH buffers and stabilizers, an ingredient in pharmaceutical products, food and personal care products and as a chemical intermediate.
TECHNICAL GRADE
APPEARANCE
white to off-white crystalline powder
ASSAY (DRY BASIS)
97.5% min
LOSS ON DRYING
1.0% max
HEAVY METALS
20ppm max
FOOD GRADE
APPEARANCE
white, odorless, crystalline powder
ASSAY (DRY BASIS)
98.5% min
IDENTIFICATION
passes test
LOSS ON DRYING
CHLORIDE
0.002% max
HEAVY METALS
20ppm max
OTHER INFORMATION
Glycine is a white, crystalline amino acid; dissolve in water and. As also known as aminoacetic acid, it is the simplest amino acid. It has acid group as well as amino group which both groups act as a base. It is not optically active, i.e., it does not have d- and l-stereoisomers as two hydrogens are bonded to the central carbon atom. It is nonessential amino acids for mammals; i.e., they can synthesize it from amino acids serine and threonine and from other sources and do not require dietary sources. It is commercially synthesis from ammonia. It is also prepared from bromoethanoic acid by reaction with potassium phthalimide. It helps to improve glycogen storage utilized in the synthesis of hemoglobin, collagen, and glutathione, and facilitates the amelioration of high blood fat and uric acid levels.